Source: https://www.intelligentliving.co/links-to-depression-how-to-prevent-reduce-it
For several decades scientists have seen a distinct association between inflammation and depression. Various autoimmune conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease, have been steadily linked with higher rates of mood disorders, while chronic, low-grade inflammation has been linked with lower dopamine levels and motivation. However, there is still significant debate over what kind of causal mechanism could directly connect inflammation with depression.
Histamine
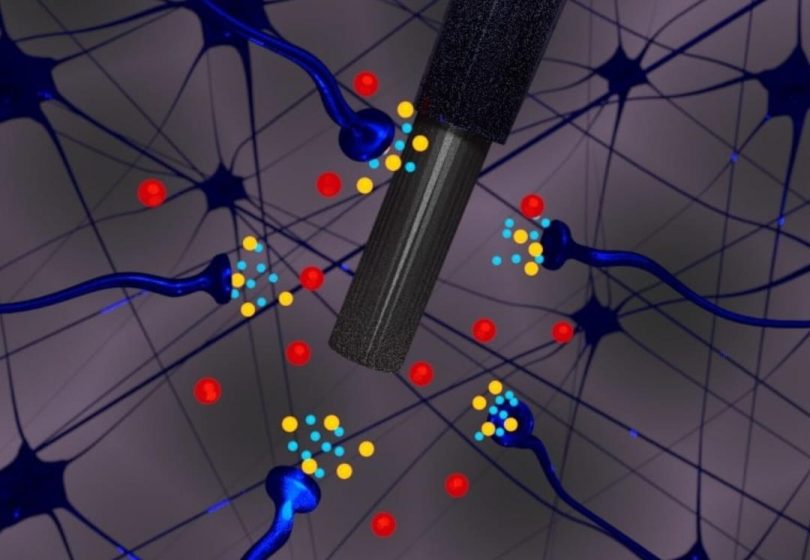
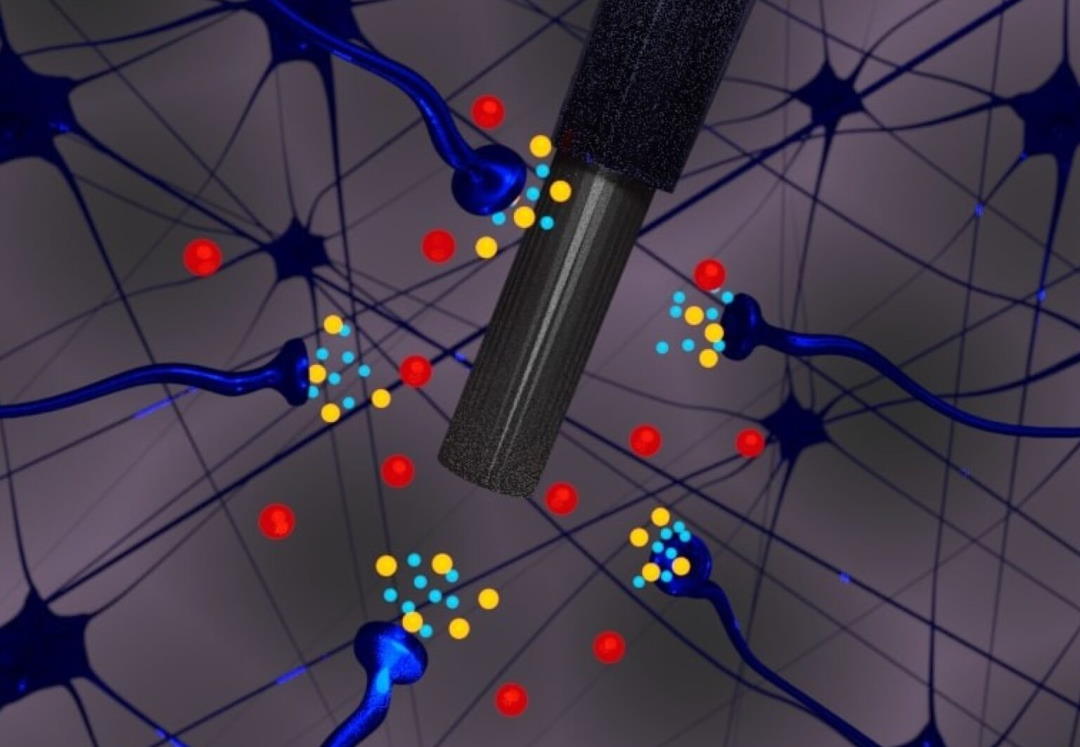
A new robust study conducted by an international team of scientists has discovered one possible missing link clarifying how inflammation leads to depression. Through a series of mouse experiments, the team found evidence that inflammation-induced histamine activity can inhibit the release of serotonin in the brain. Thus, the findings suggest histamine may play a significant role in triggering depression.
The scientists started by making a new kind of microelectrode that can be implanted in the hippocampus of mice to measure serotonin levels, a critical mood-regulating neurotransmitter, in real-time. Serotonin is often focused on as a therapeutic target for depression.
Next, the team injected the mice with a toxin that triggers inflammatory responses to investigate how inflammation impacts serotonin activity. Within only minutes, serotonin levels were seen plummeting in the animals’ hippocampus. Since the toxin used in the experiment cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, the researchers were confident that inflammation was responsible for the serotonin reduction.
Further investigations led to the researchers discovering that increased histamine levels in the brain, produced as part of the animals’ inflammatory response, caused the reduction in serotonin levels by “acting on inhibitory histamine H3 heteroreceptors on serotonin terminals.”
The next phase of the experiment involved administering the animals’ escitalopram, a common anti-depressant drug belonging to a family known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). However, serotonin levels did not increase in the animals treated with the inflammatory toxin SSRI administration. Instead, the anti-depressant’s effect was blunted since it hindered the brain’s ability to clear histamine, interfering with the regulation of serotonin levels.
Finally, the researchers treated the animals with histamine-reducing drugs alongside the anti-depressant to confirm this potential mechanism. And sure enough, this combination of drugs saw serotonin levels increase in the inflammation-induced mice.
Our work shines a spotlight on histamine as a potential key player in depression. This, and its interactions with the ‘feel-good molecule’ serotonin, may thus be a crucial new avenue in improving serotonin-based treatments for depression.
People who have or know someone with allergies and hay fever are familiar with histamines. These molecules play a significant role in the body’s immune response to foreign pathogens and influence sleep cycles, sexual function, and blood pressure.
Standard anti-histamines that are available over-the-counter for allergies work by hindering the ability of histamine molecules to bind with specific histamine receptors. Therefore, it is essential to note that these common anti-histamines for allergies do not affect this newly discovered mechanism.
Instead, in this study, the scientists used drugs that completely stifle histamine levels across an entire body. Therefore, since histamine is vital for various bodily functions, it is not feasible to translate these findings to humans just yet.
In addition, this research, published in the journal JNeurosci, was only conducted on animals. That said, more work is needed to confirm whether the exact mechanism is at play in humans. Nevertheless, the team suggests that it is possible this inflammation-induced histamine mechanism could help shed light on some of the inconsistencies in SSRI anti-depressant effectiveness from patient to patient.
However, suppose it can be validated in humans, and a pharmacological target is identified. In that case, new depression treatments can be developed, including ones that boost the efficacy of currently available SSRI drugs by preventing histamine from disrupting serotonin levels.

Hashemi explained:
Inflammation is a whole-body response and is therefore hugely complex. Depression is similarly complex, and the chemicals involved are affected in myriad ways by both genetic and environmental factors. Thus, we need to look at more complex models of depression behaviors in both mice and humans to get a fuller picture of both histamine and serotonin’s roles in depression.
Air Pollution
According to a study on the effects of urban air pollution on mental health, increases in people’s exposure to air pollution are linked with significant rises in anxiety and depression.
The study, published last year in Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, shows that a gradual increase in nitrogen dioxide, mainly produced by diesel vehicles, amplifies the risk of common mental disorders by 39%. While tiny particle pollution (also called PM), mainly from burning fossil fuels and tire dust, causes the risk to rise by 18%.
People living in higher PM levels were twice as likely to experience mental health issues than those living in the least polluted zones. However, the researchers acknowledged that other significant factors cause mental health, such as childhood experiences or genetics.
Interestingly, a different team led by Nanjing Medical University researchers discovered that depression could also be inherited via RNA in sperm. Regardless, unlike these other factors, air pollution could be prevented.
Smoking Tobacco
There are many reasons why smoking tobacco is harmful, but researchers have discovered another reason people should not smoke. A 2019 study found that smoking tobacco increases the risk of depression and schizophrenia.
The evidence adds to a growing body of work, suggesting that smoking can have opposing effects on mental health. For example, in collaboration with the University of Amsterdam, the same team published a study in the British Journal of Psychiatry that showed evidence that smoking tobacco increases the risk of bipolar disorder.
Gut Microbiota
Unhealthy gut microbiota can lead to several conditions, including inflammation and depression. For example, a 2019 study found that two different gut bacteria are depleted in people with depression, regardless of anti-depressant treatments. They discovered this from the first population-level study on the link between gut bacteria and mental health, precisely quality of life and depression.
Therefore, what you eat is significant. A good diet full of fiber and varied fruits and vegetables is vital for a healthy gut microbiome. Aside from fighting depression, making the right food choices can also help control histamine levels and combat inflammation.
Foods to Control Histamine Levels
A healthy diet comprises moderate histamine levels. However, some foods that are high in histamine can trigger inflammatory reactions and other negative symptoms.
Histamine-rich foods to avoid:
- Alcohol and other fermented beverages;
- Fermented foods and dairy products, like yogurt and sauerkraut;
- Dried fruits;
- Avocados;
- Eggplant;
- Spinach;
- Processed or smoked meats;
- Shellfish;
- Aged cheese.
Foods that activate histamine release in the body:
- Alcohol;
- Bananas;
- Tomatoes;
- Wheat germ;
- Beans;
- Papaya;
- Citrus fruits;
- Nuts, specifically walnuts, cashews, and peanuts;
- Food dyes and other additives.
People who have histamine intolerance should incorporate low-histamine foods into their diet to help reduce negative symptoms. However, keep in mind that a histamine-free diet does not exist.
Here are some of the best foods to eat that are low in histamine:
- Fresh meat and freshly caught fish;
- Non-citrus fruits;
- Eggs;
- Gluten-free grains, like rice and quinoa;
- Dairy substitutes, such as almond milk and coconut milk;
- Fresh vegetables except for spinach, avocados, tomatoes, and eggplant;
- Cooking oils, like olive oil.
Foods To Fight Inflammation
Aside from depression, inflammation can result in many harmful health conditions, like cancer, heart disease, and obesity. What you eat plays a big part – it can either reduce inflammation or cause it.
A minor inflammation is natural because it’s part of the body’s immune response necessary for healing. However, when it’s out of control, that’s when serious health issues occur. So, here are some tips and a list of the best things to eat that will keep your inflammation levels to a minimum.
First: Eliminate foods and beverages that cause inflammation, including high-sugar, processed, and fatty foods (like doughnuts, fried chicken, and soda, for example).
Second: Incorporate foods that curb inflammation. These include:
- Oily fish- such as anchovies, herring, mackerel, salmon, sardines, and tuna.
- Whole grains- Avoid refined white bread, rice, cereal, and pasta. Instead, consume whole grains.
- Dark leafy greens- such as broccoli, brussels sprouts, kale, spinach, and swiss chard.
- Avocados.
- Nuts.
- Peppers.
- Tomatoes.
- Beets.
- Turmeric.
- Garlic and onions.
- Extra virgin olive oil.
- Parsley.
- Berries.
- Green tea and Matcha.
- Dark chocolate and cocoa.
Foods To Combat Stress And Curb Depression
Some foods help relieve tension more than others, while the lack of some stress-fighting foods can make you feel worse (like anxiety, depression, and panic attacks).
Of course, occasional bouts of stress are usual. But chronic stress isn’t, and it can lead to severe health problems not only mentally but physically too (like heart disease). So, to help, here’s a list of some of the best things to eat that will keep your stress levels to a minimum.
Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach and other leafy vegetables contain a vitamin called folate (also known as folic acid or Vitamin B9) that reduces the risk of depression symptoms.
Sweet Potatoes: Sweet potatoes are a great source of whole, nutrient-rich carbs, vitamin C, and potassium, helping lower stress hormone cortisol levels. Chronic stress can lead to cortisol dysfunction, resulting in pain, inflammation, and other adverse effects.
Artichokes: Artichokes are high in magnesium, potassium, vitamins C, and vitamin K, all of which are essential for a healthy stress response. On top of that, they’re especially rich in prebiotics, a type of fiber that feeds the good bacteria in your gut.
Artichokes contain a concentrated amount of prebiotics like fructooligosaccharides (FOSs), which have been shown to reduce stress levels in animal studies. Another study demonstrated that people who consumed five or more grams of prebiotics daily experienced improved depression and anxiety symptoms.
Broccoli: Eating broccoli or other cruciferous vegetables can reduce your risk of mental health disorders as well as certain cancers and heart disease. Broccoli can be considered a superfood with concentrated nutrients, including stress-fighting magnesium, folate, and vitamin C.
Another excellent thing broccoli provides is a high amount of sulforaphane – a sulfur compound with neuroprotective properties. In addition, it may offer anti-depressant and calming effects – and vitamin B6, which is linked to a lower risk of depression and anxiety in women if taken in higher amounts. One cup (184 grams) of the vegetable (cooked) has more than 20% of the daily value for vitamin B6.
Blueberries: Blueberries are high in flavonoid antioxidants, which provide powerful neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects. Eating flavonoid-rich foods may protect against depression and improve your mood.
Organ Meats: The heart, liver, and kidneys of animals are an excellent source of B vitamins – especially B6, B12, folate, and riboflavin. These vitamins are essential for stress control because they produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine that regulate mood.
Turkey Breast: Turkey breast contains the amino acid tryptophan, which helps produce serotonin – the chemical that regulates feelings of well-being, happiness, and hunger. Other foods high in tryptophan include beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, oats, tofu, fish, and eggs.
Fatty Fish: Fatty fish like herring, mackerel, salmon, and sardines are high in mood-enhancing omega-3 fats and vitamin D. Omega-3s are so essential for brain health that low omega-3 intake may cause increased anxiety and depression. Similarly, low levels of Vitamin D can result in an increased risk of anxiety and depression.
Dark Chocolate– small indulgence of dark chocolate (70% cocoa or more) may have the power to regulate your stress levels because it can reduce stress hormones like cortisol.
Chamomile Tea– The medicinal herb Chamomile has been used as a natural stress reducer since ancient times. It can be consumed to promote restful sleep and reduce depression and anxiety symptoms.
Besides making the right food choices, spending time in nature can also curb depression.
Reduce Depression By Tuning Into Nature
Nature reduces stress, anxiety, depression, and pain. This is why doctors in Scotland are writing out prescriptions for nature walks and bird watching, and the Japanese are promoting forest bathing. However, you don’t have to go to parks to benefit from nature; just listening to nature’s sounds or filling your home with mood-boosting plants could have the same effect.
A study conducted by researchers from Michigan State University, Carleton University, Colorado State University, and the US National Park Service analyzed 18 previous studies on how natural soundscapes can positively affect human health.
In the lab, the team studied audio tracks recorded at 221 sites across 68 national parks in the US. Their results, published on April 6, 2021, in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that listening to natural sounds decreases stress and pain, improves cognitive function and mood, increases concentration, and more.
Other research that shows how being near nature and spending time outdoors is good for health, happiness, and well-being include:
- A study from scientists at Cornell University found that green space in urban areas can reduce violent crime, gun violence, stress and lead to safer communities and improved health.
- Another study found that spending two hours a week in nature reduces anxiety and depression, lowers blood pressure, cuts the risk of other diseases, and boosts creative and cognitive abilities.
- Simply growing indoor plants can provide a significant mood boost and help relieve symptoms of depression and anxiety. Some of the best indoor plants that don’t require much attention, watering, and light include aloe vera, calathea rattlesnake, Chinese evergreen, air plant, peace lily, and snake plant.
- Finally, a study published in the journal Ecological Applications found that you don’t need to be near the plants to reap their benefits; just ‘seeing’ nature can positively affect health. The study followed 3,000 people in Tokyo, Japan, and found that seeing greenery from a window improved mental health.
Psychedelic To Reduce Depression
In 2019, Johns Hopkins researchers surveyed the anti-depressant qualities of DMT – a short-acting psychedelic. They reported that it resulted in extraordinarily positive improvements in self-reported depression and anxiety when given in a ceremonial group setting.
Another study, conducted last year, revealed preliminary evidence that psychedelic drugs can improve mental health by forcing individuals to confront their issues and become more accepting of distressing experiences. The research adds to a growing body of work that suggests using psilocybin substances can result in long-term improvements in depressive symptoms.
According to the study’s author Richard Zeifman, a Ph.D. student at Ryerson University, psychedelic therapy is promising as a novel treatment for a variety of mental health conditions, including:
- Anguish, associated with a life-threatening illness.
- Major depressive disorder.
- Substance use disorders.
Zeifman added:
Our results provide further support for the negative mental health effects associated with avoidance. This can be summed up with a saying that is often used in the context of psychedelic therapy, that ‘The only way out is through.’
Besides confronting your problems, other simple ways to avoid depression include:
- Reducing alcohol and drug use.
- Quitting nicotine.
- Exercising regularly.
- Cutting back on social media.
- Staying away from toxic people.
- Reducing stress.
- Minimizing your daily chores.
- Getting plenty of rest.